
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Little Folks' Handy Book, by
Lina Beard and Adelia B. Beard
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net
Title: Little Folks' Handy Book
Author: Lina Beard
Adelia B. Beard
Release Date: May 13, 2008 [EBook #25462]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK LITTLE FOLKS' HANDY BOOK ***
Produced by Chris Curnow, Joseph Cooper, Emmy and the
Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net

| ON THE TRAIL |
| THINGS WORTH DOING AND HOW TO DO THEM |
| RECREATIONS FOR GIRLS—INDOOR AND OUTDOOR |
| WHAT A GIRL CAN MAKE AND DO, AND NEW IDEAS FOR WORK AND PLAY |
| THE AMERICAN GIRL'S HANDY BOOK; or, HOW TO AMUSE YOURSELF AND OTHERS |
| LITTLE FOLKS' HANDY BOOK |

"Let me do it. Let me make it," is the cry when a child sees an older person putting together the different parts of an interesting piece of work; and it is this desire to do things himself, this impulse toward self-expression, that, when properly directed, forms so great a factor in his all-around development and education. Using the hands and brain together stimulates interest and quickens observation and intelligence, and, as the object takes form beneath the little fingers, the act of making, of creating, brings with it a delight and satisfaction which the mere possession of the same thing made by another can not give. "Look! See what I have made," comes with a ring of triumph as the childish hands gleefully hold up the finished article for inspection.
In this book we have endeavored to open a new and large field of simple handicrafts for little folk, giving them an original line of toys and a new line of materials with which to make them. We hope in these pages to bring to children the joy of making creditable and instructive toys of such ordinary things as empty spools, sticks of kindling wood, wooden clothespins, natural twigs, old envelopes and newspapers, and in this way to encourage resourcefulness,[vi] originality, inventiveness, and the power to do with supplies at hand.
Everything described in the book has been actually made by the authors, and made by such practical and simple methods that a child's mind can grasp them, and a child's hands be easily trained to manufacture the articles. It is, therefore, our hope that the "Little Folks' Handy Book" will be found useful both in Kindergarten and Primary grades of the schools and in the home nursery; a helpful friend to teachers and to mothers.
Flushing, N. Y., February 10, 1910.
| CHAPTER | PAGE | |
| I. | Paper Building Cards | 1 |
| II. | Toys Made of Common Wooden Berry-Baskets | 5 |
| III. | Straw and Paper Furniture | 9 |
| IV. | A Newspaper Boat which Will Sail on Real Water | 15 |
| V. | Paper Jewelry | 19 |
| VI. | What to Make of Empty Spools | 28 |
| VII. | Old Envelope Toys and How to Make Them | 47 |
| VIII. | Toys of Clothespins | 55 |
| IX. | Scrap-Books | 64 |
| X. | Toys Made of Common Kindling Wood | 70 |
| XI. | Little Twig People | 79 |
| XII. | Visiting-Card Houses | 90 |
| XIII. | Playing Indians with Costumes Made of Newspapers | 98 |
| XIV. | Christmas-Tree Decorations | 106 |
| XV. | A Home-Made Santa Claus | 124 |
| XVI. | Nature Study with Tissue-Paper | 130 |
Make your building cards of ordinary writing-paper. You may have as many cards as you like, though twelve are all that are used to make the things shown in our photographs.
For each card cut an oblong of paper five inches long and two and a half inches wide. This is a very good size, but you can make them a little larger or smaller. Always remember, however, to have them just twice as long as they are wide, and all of one size. When you have cut out the oblong (Fig. 1) fold it through the middle, bringing the two short edges evenly together. The dotted line in Fig. 1 shows where it is to be folded. Now open the oblong half-way and you will have the building card (Fig. 2). They are very simple and easy to make, aren't they? But wonderful and delightful things[2] can be built with these pieces of paper. You can have a whole camp of little tents by standing the cards with the folded edge up; and to make
The second illustration (Fig. 3) shows just how to do this. Use the tents again for
The third and top story will be one tent, which forms the[3] peak of the pyramid. Of course you can make your pyramid very much larger by adding more tents to the first row and then building it up higher.
Build
Use a one-quart wooden berry-box for the china closet (Fig. 7). Turn the empty box facing you, and slide the prongs of a clothespin up through the open crack at the lower right hand of the box. Allow one prong of the clothespin to come on the outside and the other prong on the inside of the thin wooden side of the box; adjust the clothespin well to the front edge of the box, and it will form the right-hand front leg of the china closet. Add another leg in like manner on the same side of the box for the back leg; then slide two more clothespins up on the opposite side of the box to form the remaining two legs (Fig. 8).
The prongs of the clothespins do not reach up to the top of the inside of the box, but leave sufficient space for a shelf.[6] Make the shelf by laying a clothespin across from side to side, supported by the prongs of the back legs, and another across, supported by the prongs of the front legs (Fig. 8). The clothespin used for the front of the shelf will probably have to be a trifle longer than that for the back, as the box is wider in front than at the back. Set some toy dishes on the top, the shelf, and the inside bottom of the china closet, as in Fig. 7.
With another quart berry-box and four more clothespins make the
Slide the prongs of a clothespin down on either side of the box at the four corners (Fig. 9), then turn the table right side up, placing it on its feet. Set the table with toy dishes, and dinner will be ready (Fig. 10).
The table can be turned into a dressing-case by standing two clothespins on their heads at each side of the back of the top of the table, and sliding a piece of stiff paper across from clothespin to clothespin between the prongs for a mirror[7] (Fig. 11). Of course, the addition of a fringed white paper, or cloth scarf, over the top of the dressing-case would enhance its appearance, as would also a table-cloth over the top of the dinner table, but the covers were purposely omitted in the photographs that one may see exactly how the articles were made.
Make a
A comical little berry-basket[8]
Fig. 16 shows two clothespin horses attached to a
A handful of straws, such as are used for lemonade and soda-water, several large sheets of writing-paper, and some small-sized pins—these are your materials. A pair of sharp scissors, a ruler marked off into whole, half, and quarter inches, and a lead pencil—these are your tools.
We will begin with the old-fashioned four-post bedstead with its canopy and valances (Fig. 17). It is easily put[10] together, but you must be careful to cut the straws for the posts all exactly the same length, making them about seven inches long, and to have your measurements for the other parts quite correct, in order that the bedstead may stand perfectly upright. Select four straight straws for the posts—sound and whole. Split straws will not do.
The mattress and canopy are exactly alike; each has its valance, and they are just the same size; so directions for one will answer for both. Cut an oblong of writing-paper eight and a half inches long and six and a half inches wide. Be sure that the ends and side edges form perfect right angles; if they do not, the bed will be crooked. The edges of your sheet of writing-paper are at right angles to one another, and if you use the top edge of your paper for the top edge of your oblong, and the side edge of the paper for one side edge of your oblong, the rest will come out all right.
Now draw perfectly straight lines across your oblong from top to bottom, just one and a half inches from each edge (Fig. 18). Then from side to side draw two more straight lines; the first one and a half inches below the top edge and the other one and a half inches above the bottom edge. This gives the mattress with a border all around. In each corner of the mattress, a little more than a quarter of an inch from the end and side lines, draw a small cross as shown in Fig. 18. Be sure these crosses are placed correctly, and are exactly alike in mattress and canopy. Now cut out the four squares at the corners of the oblong, as indicated by the heavy lines in Fig. 18, and insert the point of your scissors[11] in the centre of each little cross and snip along each line of the cross. Do not make the slashes too deep.
Cut the edges of the border, or valance, into small points, as in Fig. 17; then bend the valance down at the sides and ends of the mattress. The dotted lines in the diagrams show where to bend the paper. Make the canopy just as you have made the mattress, but cut deeper points on the edge of the valance.
Through each of the four straw bedposts run a small pin two and a quarter inches from the end of the straw (Fig. 19).
Push the long ends of the straws up through the slashed crosses in the corners of the mattress (Fig. 19) until the bottom of the mattress rests on the pins, then run a pin through each straw just above and close to the top of the mattress. Between the two pins the paper can slip neither up nor down. Run another pin in each straw post half an inch from the top, slide the canopy down upon these, and fasten with more pins, as you did the mattress. Make the bolster by folding a piece of paper the proper shape and cutting the end edges in points for trimming.
Now you not only know how to make the bedstead, but
Make the legs of the table three inches long. Cut the top of the table four inches long and three and a half inches wide, and the shelf three and a half inches long and three[12] inches wide. Measure one-quarter of an inch from each edge of the table top and draw straight lines as in Fig. 21. This will give you a narrow border all around the top.
Make and cut the little crosses in the corners of top and shelf, then cut out the squares at the corners of the top and bend down the edges. The shelf of the table should be one inch above the bottom ends of the straws, and the top of the table one-quarter of an inch below the top ends of the straws.
By making the straw legs of the table twice as long, and the top and shelves narrower, you can have another useful article of furniture, for by adding two shelves of paper on[13] the straws, and fastening them in the same way, this can be used as a cupboard or shelves on which to place the tiny doll dishes or clothes. The table can also be made into a little dressing-table, by simply using for the back legs straws twice as long as the front legs and then slipping a square piece of paper on the straws that extend above the table, to serve as a mirror. Just as the paper is slipped on the straws for the back of the chair (Fig. 22), silver paper is pasted on this to make it look like glass.
With these few patterns you can make any number of useful articles to furnish Miss Dolly's house. You can make small beds and large beds, small tables and large tables, and many sizes of chairs.
You can make
This furniture will be especially useful in playing with paper dolls, and by using different colors, in colored papers, you can have a blue room, a pink room, and a green room.
You can make tissue-paper sheets and spread for the bed and pillow-slips, too, if you like. Thus dolly can be tucked away snugly for the night.[14]
The ingenuity exercised in the construction of these simple articles will encourage the development of deftness and skill in the little fingers, which are ever ready to imitate anything that teacher can make.
You can fold a thirteen-and-a-half-inch square of newspaper into a fine boat measuring thirteen inches from stem to stern. It will be a good, stanch craft like Fig. 25, to float and sail out in the open on pond, lake, or river, or at home in basin or bath tub.[16]
| blah | center |
Cut your square of paper even and straight. Place it out flat on top of a bare table and fold at the centre along the dotted line (Fig. 26), which will make Fig. 27. Bend each side of this down outwardly along its centre at the dotted line and bring the edges a quarter of an inch lower than the bottom fold A; then your paper will be four layers like Fig. 28. Turn up the lower edge B of Fig. 28, making Fig. 29. Fold back the three lower layers of the corners at the dotted lines (Fig. 29) and you will have Fig. 30. Bend back the upper corners at the dotted lines to make Fig. 31. Open Fig. 31 at the top and it will be your boat. Turn the boat upside down and slide one[17] loose edge on the bottom under the other loose edge; then pinch each bottom point and bend it down toward the centre of the boat, creasing it flat (Fig. 32). Turn the boat right side up again, set it on the table, bend the two sides well up and crease them along the bottom until the boat resembles Fig. 33.
To render the craft water-proof melt a piece of wax candle, turn the boat upside down again and give the bottom a coat of the melted white wax, extending the coat half way or more up the sides. Use a teaspoon for pouring the wax over the[18] boat; the hot wax soon hardens and in a few moments you may launch the little craft on the water.
If you want to make a
With thread and needle take a stitch or two in the lower corner of the sail and attach it with a short length of the thread to the stern; fasten securely. Also fasten the pennant to the mast, so that it cannot turn, for in this vessel both sail and pennant must be stationary and not swing to either side. Be careful not to have the sail too heavy.
Ordinary brown wrapping paper is the best to use for this paper jewelry. Indeed the pale, creamy yellow of some wrapping paper is much like ivory in color, and the chains and ornaments made of it are really charming.
See how simply the necklace is made without glue or paste. It is a system of double rings that shift and slide in one's hands like the links of a metal chain. When the principle is understood it is all very easy.
The rings may be cut out free-hand by folding the paper as in Fig. 34. Cut an oblong about six inches long and three inches wide and fold it crosswise through the middle, then bring the two side edges together and fold it again lengthwise. Start at the top where the paper is folded and cut out the ring as in Fig. 34. You will notice in the drawing that the circle at the top is slightly elongated; this is necessary in fitting the rings together. The ring when opened will look like Fig. 35. Cut out six rings the size and shape of Fig. 35, then make two smaller ones, like A (Fig. 36), and eight still smaller ones, like B (Fig. 36). Now cut a single ring perfectly round, a trifle larger than Fig. 34, a double ring like C (Fig. 37), and a pearl-shaped pendant like Fig. 38. Open Fig. 38 and cut the three-cornered catch in one half and the slit in the other half, as shown in Fig. 39. Cut the catch first, then fold the pendant again, as in Fig. 38, and punch[20] small holes with a pin at the base of the catch through the other half, to mark the place for the slit. The slit must not be as long as the base of the catch, else the catch will not hold.
 The little queen. Adorned with paper jewelry.
The little queen. Adorned with paper jewelry.
Put the necklace together by slipping the half of one ring over both halves of another, as in Fig. 40. Commence with the single ring. Slip half of a large double ring through the single ring, bring the double ring together and slip another large ring through that, then add another large ring and you will have a chain of three large rings with the single ring at the end.
[21]To the end double ring attach a ring, like A (Fig. 36); to A add a chain of four rings like B (Fig. 36). This gives you[22] just half of the necklace, for the single ring is to be the middle one. Make the other half in the same way, starting on the opposite side of the single ring and slipping ring into ring as you did before. Attach the ring pendant, C (Fig. 37), to the single ring between the two side rings, then add the pendant. Fasten the two halves of the pendant together by folding the two points of the catch inward, slipping the catch through the slit and then spreading the points out again flat. This makes a very secure fastening and, unless the neck of the catch is too slender, it will neither break nor pull apart.
Fig. 41 is the clasp for the necklace. Cut it out like the pattern and make it about three inches long. Slip one end of the clasp through the last ring on one end of the necklace, the other end of the clasp through the last ring on the other end of the necklace, then bring the clasp together and slip the catch through the slit, as in Fig. 42. The photograph (Fig. 43) shows how pretty the necklace is when finished.[23]
The coronet shown in the illustration of the "Little queen" is cut in one piece (Fig. 44). At the widest part, from top to bottom, it is three inches wide, and the ends may be lengthened or shortened to fit any head. The ends must meet and fasten at the back.
Little rings, one inch in diameter, cut like Fig. 45, ornament the coronet, as shown in Fig. 44. They are fastened by the catch at the top through slits cut in the coronet. Make three slits, one below the other, a little over one inch apart, down the middle of the coronet, and on either side of these make six more slits in the position shown on the right half of Fig. 44. This gives fifteen slits, for which you must have fifteen rings. These dangling little rings that shake and twinkle with every movement are fascinating little ornaments, and are far prettier than more elaborate designs.
Quite oriental-looking ear-rings are made like Fig. 46. Cut first two single elongated hoops like Fig. 47, making them almost three inches long and one and three-quarter inches from side to side. These long hoops are to slip over the ears to hold the ear-rings on. Cut two hoops, like D (Fig. 46), and two pendants, like E (Fig. 46). Fasten the hoop D upon the hoop (Fig. 46), and the pendant E upon the hoop D, clasping the pendant by its catch as you did the pendant of the necklace. The children need not follow exactly the shapes of the "danglers" and pendants shown here—let them exercise their own taste in these.
[24]The bangle bracelet (Fig. 48) is made as in Fig. 49. Cut a strip of paper half an inch wide and about eight inches long;[25] make a catch at one end and a slit in the other end, then a little below the middle cut six slits half an inch apart, as in Fig. 49.
Cut six round charms, three-quarters of an inch in diameter, with a catch at the top like Fig. 50, and fasten the charms on the bracelet. Fig. 49 gives the inside of the bracelet with three charms attached. This bracelet is large for a small child, but can be shortened at the end to fit any little arm.
 Playing lady. The lorgnette.
Playing lady. The lorgnette.
Fig. 51 is a link bracelet. Make this by folding a strip of paper eight inches long crosswise through the middle. Bring the folded end half way down and fold, turn back the other[26] end and fold like a fan. This divides the paper into six equal parts. Now cut out the outer edge of all the links at once. Free the two end links and cut out the centres of the others, then cut the centres of the two links, as shown in Fig. 51, making the catch and slit like the pattern.
The links of the long chain shown in the photograph of "The queen and her captive," are cut exactly like the bangle bracelet (Fig. 49). The slits and charms are, of course, omitted. Fig. 52 shows how the chain is put together by slipping one link through another and fastening it with its catch. You can make the chain any length. It is so strong that only rough handling will pull it apart.
Now comes the lorgnette, which works beautifully made of rather stiff paper. Make the case of a strip of paper three[27] inches wide and eight inches long. Fold the paper lengthwise through the middle and cut it, rounding at the top like Fig. 53. In one side cut a small round hole at the top, rather near the edge of the case, F (Fig. 53), and fold back the lower corners according to the dotted lines. Cut out the eyeglasses like Fig. 54. Curl the edges of the ball G together and slide the ball through the hole F in the case, as in Fig. 55.
The glasses swing quite loosely by this hinge, and will slide easily in and out of the case. When tucked away inside the case a little flirt of the hand, a turn of the wrist, will throw them out and they can be lifted to a piquant little nose in the most approved and fine-ladylike fashion.
The lorgnette in use is shown in the photograph, "Playing lady." "The little queen" displays jewelry, and "The queen and her captive" show the long chain.
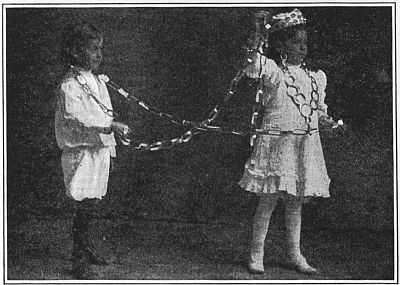 The queen and her captive.
The queen and her captive.
Gather up all the spools you can find, big, little, thick, and thin; no matter how many, you can use them all. There is no end of fun to be had with these always-on-hand, easily found toys; they may be made into almost everything.
Make the yard into a cheerful
The trees are easy to make and are very effective; they are simply fringed strips of paper rolled like a paper lighter with the large ends stuck into spools. Cut a strip of green tissue-paper fifteen inches long and five wide; then cut one-third of the strip narrow, about one inch wide, and fringe the remaining two thirds (Fig. 64). With the thumb and first finger of your right hand begin to roll the corner as shown at A (Fig. 64). Continue rolling, and the fringe, which forms the foliage, will stand out on the outside of the rolled part or trunk of the tree. When you reach the solid, narrow part of the paper strip it will roll into a smooth, round stick, forming the lower part of the tree trunk. Paste the last wrapped corner of the paper roll in place and clip the tree trunk off even across the bottom edge; then press it into a hole in the centre of an empty spool of ordinary size, and there's your tree! You can vary the foliage by crimping the fringe with knife or scissors before the strip is rolled into a tree and by having the fringe of some much longer than that of others. If you use different tones, tints, and shades of green, running from very light to dark, and make a lot of them varying in height, the trees will look very pretty and they can form a jungle where toy wild animals can live; or a number of the trees might form a playground or a grove where dolls may go for a picnic.
In the photograph of the group of trees you will see a number of pots of flowers. The flowers are disks and squares of different bright-colored tissue-paper, each one with its centre pinched together and twisted into a stemlike piece, which is pushed down into a buttonhole-twist spool. Around some of the flowers a smaller square of green may be used for foliage.[32]
You could make an extensive flower garden by using a great number of these short, flat spools and bits of gay tissue-paper, and they can be arranged and rearranged in many different ways.
It is possible to make all kinds of toy furniture of spools. If you want
A little table can be made in a moment's time. All that is necessary is to choose a large spool and place a round piece of paper on the top (Fig. 66). Make the bureau of six spools close together in two rows of three spools each, and cut the top of a piece of paper with a high extension in the centre, which you must bend upright for a mirror. The washstand can be four spools quite close together covered with a piece of paper. A piano is easily made, but you must think it out for yourself. Use a small spool for the piano-stool.[33]
You can glue the tops on the table and washstand and the mirror on the bureau also; though this is not necessary, for if you are careful and do not knock against the furniture it will remain secure.
Now make the toy
See how firm and substantial the little kitchen furniture looks in the photograph with its fine stove, dresser, and wash-tub (Fig. 68). Use four spools for the feet of the stove. Over these lay a piece of pasteboard about six inches long and four inches wide, allowing it to project beyond the front feet to form the apron; then build on the body of the stove, making it of spools two layers deep, as in Fig. 69. Cut a piece of pasteboard to fit over the spools for the stove top, and have it long enough to stand out a short distance at the back; then you can build on the stovepipe (Fig. 70).
Make the dresser of spools and strips cut from pasteboard boxes (Fig. 71).[35]
For the tubs stand four spools close together, and set a little round box on top of them. Make the washboard of a piece of paper folded many times backward and forward, fan fashion. After carefully creasing the folds, pull the paper out slightly and put it in the tub for the next washday (Fig. 68).
After cooking,
When enough furniture has been manufactured, build
Cut Fig. 73 from heavy paper or cardboard that will fold without breaking. Bend all the dotted lines and cut all the heavy lines in the pattern. Push a burnt match, or a wooden toothpick through one hub, then through an empty spool[37] and the second hub. The spool forms the wheels. Screw a small pin cautiously through each of the two projecting ends of the match, piercing the wood and leaving the head and point of the pin standing out (Fig. 74). Tie a knot in the end of a string to prevent its sliding out and thread it through the hole in the dashboard.
By laying narrow strips of paper on a table or on the floor to form a boundary line, you may make a
Leave an open space for the doorway at the opposite end of the room from the organ. Build up a column of four large spools at each side of the space and connect them with a strip of paper laid from the top of one column to the top of the other.
Build the fine, large pipe-organ close to the edge of the back room. Stand eight spools in a row tight to each other at equal distances from each boundary side line. Build the[38] row up three spools high, then skipping the end spools, build on two layers of six spools each; again skip the end spools and build on a layer of four spools. Crown the last layer with two top spools. Across the centre front of the organ stand a row of spools, two high and three long. Over them lay a piece of paper bent lengthwise through the centre for the key-board and music-rack. Bend another piece of paper for the music and stand it on the key-board against the rack. Make the organ seat of two spools placed side by side in front of the organ with a strip of paper laid over them. Let the seats for the doll children be rows of three spools each. Place the seats one in front of another in parallel lines a short distance apart and allow a wide, lengthwise central aisle between them. All this is shown in Fig. 75.
Hunt up an old pasteboard box, for you will need a box lid about fifteen inches long and eight inches wide as a foundation for the realistic trolley car (Fig. 76). Use eight spools[39] for the wheels; place two spool wheels near the front and two near the back on each side. Lay the spools down flat and rest the edge of the box lid on the body of the spools; then stand a row of eleven spools on each side of the top of the box lid. Beginning at one end of the row, build up every other spool into three-spool columns; the intervening spaces form the open windows of the car.
Leave windows on the opposite side of the car in the same way, and place a row of spools close up against the bottom spools of each side of the car to form the car seats. Roof the car with a piece of cardboard cut off square at one end and rounded at the other. On top of each side of this roof place one row of six buttonhole-twist spools, the spools of each row separated equal distances (Fig. 76). Stand a spool on the front of the car platform for the motorman's wheel and you have a car like that in the photograph.
When the trolley is taken apart use the spools in building
Fig. 77 shows that the piers can be built to a good height and be solid and substantial.
Stand three large-sized spools together, forming a triangle, with one point turned to face the opposite pier. This group of three spools is the foundation of one of the two columns, which together form one pier of the bridge.
About two inches distant and on a line with the triangle of spools stand a group of three more spools, and build up each group into a column four spools high. You will need two more columns for the opposite pier of the bridge; build them as you did the first, and place the second pier exactly opposite to and as far from the first as you desire the span should reach—say about fourteen inches.
Lay a strip of pasteboard six inches wide across from pier to pier, allowing the ends to rest on the piers, but not extend beyond the outside end edges of the piers; then if your span[40] is fourteen, inches long, cut from a pasteboard box two more strips fourteen inches long and of the same width as the span; score each strip across one end, one inch from the edge, bend slightly and fit the bent edge of each strip on one end of the bridge, allowing the other end of the strip to extend away from the pier and rest on the floor, forming an inclined approach to the bridge proper as in Fig. 77.
When your pasteboard strips are well settled in place, continue building up the piers on top of the pasteboard, making each group of three spools two layers high; then build up one spool two layers high on top of the four columns.
Complete the archway by spanning the two columns of each pier with a narrow strip of stiff white paper bent up into a point at the centre and out into a flap at each end (Fig. 78). The flaps[41] rest on top of the spools. The photograph shows how the entire bridge should look, and in the photograph you will find a little lady hurrying across the bridge on her way home, and following in her wake Mr. Clothespin and Mrs. Clothespin. A paper boat under the bridge would make the scene more realistic.
Next build
If you have enough spools, you can make a miniature representation of one of the most beautiful temples ever built. Begin by standing four spools in a row for the first end of the building, allowing about the width of a spool between each two. Place eight in a row for the first side, four for the other end, and eight for the second side (Fig. 80). Have the spools all of the same size, that the walls may be alike and perfectly even, because, as you know, the walls are to be formed of columns, not as many as in the original, but enough to give an idea of the Greek temple. Build up the spools three deep into pillars; then lay a piece of pasteboard on the top of the columns for a ceiling. Bend another piece of pasteboard[43] lengthwise through the centre for the roof, and stand it tent-like on top of the ceiling. You can measure the correct size of the ceiling by laying a piece of pasteboard down flat on the floor along the eight-columned side of the Parthenon to obtain the length, and placing it flat on the floor across the four-columned side to mark the width. Make the roof the same length and a little wider than the ceiling, to allow for the height of the bend through the centre.
You must imagine a space immediately beneath the roof of the little Greek temple filled in with the most beautiful statuary, and think of the spools as white marble columns, and you should see, in fancy, another row of stately columns inside the ones you have built. Tell all about the real[44] Parthenon and hunt up a picture of the temple that all may see just how near you came to making the little model look like the wonderful Parthenon on the Acropolis, in Athens.
After admiring the building for a while, pretend that a left-over spool
You can
Now try
Take another empty spool and stick a common wire hairpin partially into the hole, bend the hairpin slightly down against the edges of the hole, do the same with three more hairpins, and you will have a spool with a funnel-like opening of hairpins at the top (Fig. 84). In the funnel place a small, light-weight ball made of a crushed bit of bright paper wound around with thread. Raise the spool to your lips and blow gently (Fig. 85). The ball will rise and fall in mid-air, in the same way that you have seen one of rubber dance at the top of a small fountain or jet of water.
Don't throw away your old envelopes; see what amusing toys can be made of them simply by folding and cutting. No paste or glue is needed, and any one of the toys given here can be made in five minutes or less.
The frog is one of the simplest and at the same time the funniest of the collection. Fig. 86 gives a side view in which his beautiful open mouth can be seen to advantage. Fig. 87 shows him sprawled out on the table. Fig. 88 gives the pattern of the frog as it appears when drawn on the envelope. You will notice that the bottom fold of the envelope is used for the top of the animal. Draw the outlines as in Fig. 88, then cut along the lines you have drawn. The under part of the body follows the edge of the lower lap of the envelope from front to hind leg. Now flatten out the fold at the top and bend the paper under at the corners,[48] which forms the head and tail. Cut a slit along the folded edge of the head for the mouth, pull the lower part down and the mouth will open wide as a frog's mouth naturally does. By working the lower jaw the frog can be made to snap at imaginary flies. Draw the eyes as shown in Fig. 87 and bend down the lower part of the body along the dotted line, shown in Fig. 88, spread out the hind legs, and Master Frog is finished.
For the little bed (Fig. 89) use a long envelope. If the top lap is open, cut it off. Flatten out the bottom fold as you did[49] for the frog's back, then bend the ends and sides as in Fig. 90. Bend up the points at each end for head and footboards, and there is your bed.
Make the table (Fig. 91) of a smaller envelope in the same way, but leave the points extending out at the ends (Fig. 90) and cut short legs on the bottom edge (Fig. 91).
Plates and other dishes can be made very easily. For circular dishes use a cent or a ten-cent piece for a pattern. Very effective cups and goblets can be made from old pieces of tinfoil. The table, however, is strong enough to hold the little china or tin dishes usually found among a child's collection of toys.
The comfortable little high-backed sofa (Fig. 92) is made of a long envelope with the top left open. Fold the envelope[50] into the box shape, as for the bed, with the points turned up. Then fold the tips of the points inward, as in Fig. 93. Now reverse the box and slit down the two front edges which gives an opening in front. Bend down this front piece and cut it off on a line with the two ends.
A deep, low-seated arm-chair can be made of an oblong envelope of ordinary size by following the directions for the sofa and allowing the back to curve instead of making it flat, then slitting down the sides and bending them over to form the arms (Fig. 94).
[51]A little bath tub, but one that will scarcely hold water, is shown in Fig. 95. In this the upper lap is left open, the[52] points are bent under, and the sides left to curve naturally. A baby carriage can also be made in this way, but for the carriage the points must extend down and have wheels drawn on them and the tips must be cut off squarely at the bottom so that the carriage will stand. The lap is the back and the handle in one (Fig. 96).
The little bungalow (Fig. 97) is something very different, yet it, too, is made of an envelope. Though it appears to have many parts it is all in one piece. The envelope is a long one, such as is used for legal papers. Fig. 98 gives the pattern. The heavy lines show where to cut and the dotted lines where to bend. The lap forms the front porch, but the porch may be left off entirely if the envelope has been slit at the top in opening it. With a little care, however, many envelopes can be opened intact. Cut along the heavy lines of the door and windows, then open the door and the little shutters. Bend back the ends of the house and in the middle of each end take a little plait from top to bottom. This is to make the ends narrower and give room for the roof to slant. Bend the roof back from the eaves along the dotted line. The back of the bungalow is made like the front, except that it has no door, windows, or porch.
Children who have a knack at drawing can greatly improve the bungalow by drawing the slats to the blinds, drawing in the panelling on the front door, putting on the knob, putting shingles on the roof, etc., etc.
The little cart (Fig. 99), that will hold quite a heavy doll, and can be trundled about like one made of wood, is not cut at all.
Fold an oblong envelope into the box shape (Fig. 93), with points turned up, but let the points be deeper than for the bed or sofa. This is because the ends of the envelope are to form the sides of the cart and must be longer from front to back. Bend the tips of the points in and crease the folds sharply that they may lie flat against the sides. Sharpen one end of a small, round stick and push it through the middle of the folded point on one side, then slide a large, empty spool on the stick and thrust the point of the stick through the opposite side (Fig. 100). The stick should stand out beyond the cart about half an inch on each side, and will need no fastening.
Puncture a hole in one end of the cart, thread a cotton string through the hole, tie a large knot on the inside end and pull the string through until the knot presses close against the end of the cart. Let the string be long enough to reach easily from the floor to the little hand that will hold the other end.[54]
Besides all these toys, a baby's cradle that has rockers and will rock, a cunning little dressing-table with its mirror, boxes of different shapes and sizes, and various kinds of baskets can be made of the old envelope. Probably there are other forms it may be made to assume—boats perhaps, that for a time at least will float on the water, and animals other than the frog.
You can make cunning, soft, downy hens and roosters simply of raw cotton and clothespins (Fig. 101). The little creatures may be pure white, dark colored, or part dark and part light, according to the cotton used.
All of
| |
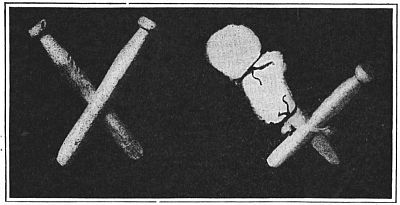
| Fig. 102—Slide the prongs of two clothespins together. | Fig. 103—Tie a piece of raw cotton over the head of one clothespin. |
With a string tie a piece of raw cotton over the head of one clothespin; have the string tight, but the cotton cover rather loose. Bring the cotton partly down the clothespin and tie it again (Fig. 103); then use your fingers to shape the top cotton into the form of a rooster's head; gently pull a little of it out to make the beak; tie a string around the beak where it joins the head, and, with thumb and finger slightly dampened, twist the end of the beak into a point (Fig. 104). Cotton which comes in sheets is best for the tail, but the other will[57] do. Lay the centre of a generous piece of cotton over the head of the second clothespin, plait the loose ends around the pin, and fasten with a string, making the edge of the tail in a line with the opening of the prongs of the pin. Cut the folded end rounded on top, and slit it up a short distance into wide fringe to form the long feathers of the rooster's tail (Fig. 104).
With another piece of cotton cover the back and sides of the rooster, as you would put a saddle on a horse. Bring the edges of the cover together down the neck and body; when fitted lift the cover, put paste here and there on its under side near the edge, replace the cover and it will stick fast; then, with the top of a wire hairpin, push the edges of the cover, front and back, in between the open prongs of the clothespin. Ink round bits of paper and paste on the rooster for eyes; make his comb and wattles of red tissue paper (Fig. 105), and you will have a fine rooster which can actually[58]
Fashion the hen in the same way you made the rooster, only have the tail smaller and without long feathers (Fig. 106). The comb on the hen must also be smaller than that on the rooster. The general shape of the hen is the same as that of the rooster. Notice that the direction of outline along the lower edge of tail and body is one continuous slanting line; remember this when adjusting the tail that it may not stand out backward at right angles from the body.
When tying beaks, ears, and tails of the various animals, cut the string ends close to the knot; then the string will sink into the cotton.[61]
To dress a
Make the
Fasten a belt high at the back and low in the front around his waist, giving the coat a Russian-blouse effect; make him a ribbon bow necktie, and ink the features.
These small people are very bewitching, as are also the animals.
You can color the sheet cotton slightly here and there with water-color paint if you are clever with a paint brush. As you work with these little dolls and animals you will find ever so many ways to vary them in effect. They are so soft and fluffy that a baby can play with them without injury, and a school or college boy may be amused by being presented with one, appropriately dressed, as a souvenir of pleasant experiences at a college luncheon or dinner.
To make a foot-ball player, finish the blouse without necktie or belt; make the shoulders wide and the hair rather short, like a college boy's rough head. So much for the boy. Paste a letter cut out of colored paper on the front of the blouse to make it look like a college sweater, and gather the trousers in a little at the knees. You can tuck an egg-shaped ball made of brown raw wool under one arm for a realistic touch, if you choose.
Little girl dolls may be similarly made to represent basket-ball players in short skirts and school or college sweaters, with appropriate emblems on the front, for a special entertainment.
Making these figures is much less trouble than dressing dolls entails, and much more of a novelty, too. They take so many shapes that they fit almost any occasion.
In fact, the possibilities of these cotton and clothespin toys are almost endless in the hands of ingenious young people.
The nursery scrap-books made of linen or colored cambric are, perhaps, familiar to most of our readers; but for the benefit of those who may not yet have seen these durable little books, we will give the following directions for making one:
Cut from a piece of strong linen, colored cambric, or white muslin, four oblongs twenty-four inches long by twelve inches wide. Buttonhole-stitch the edges all around with some bright-colored worsted, then place the oblongs neatly together and stitch them directly through the centre with strong thread (Fig. 117). Fold them over, stitch again, as in Fig. 118, and your book is finished and ready for the pictures.
It is in the preparation of these pictures that you will find[65] the novelty of the plan I propose. Instead of pasting in cards and pictures which have become too familiar to awaken interest, let the young book-makers design and form their own pictures by cutting special figures, or parts of figures, from different cards, and then pasting them together so as to form new combinations.
Any subject which pleases the fancy can be illustrated in this way, and the children will soon be deeply interested in the work and delighted at the strange and striking pictorial characters that can be produced by ingenious combinations.
Stories and little poems may be very nicely and aptly illustrated; but the "Mother Goose Melodies" are, perhaps, the most suitable subjects with which to interest younger children, as they will be easily recognized by the little folk.
Take, for instance, the "Three Wise Men of Gotham," who went to sea in a bowl. Will not Fig. 119 serve very well as an illustration of the subject? Yet these figures are cut from advertising cards, and no two from the same card. Fig. 120 shows the materials; Fig. 119 shows the result of combining them.[66]
Again, the little man dancing so gaily (Fig. 122) is turned into "Little Jack Horner" eating his Christmas pie (Fig. 121), by merely cutting off his legs and substituting a dress skirt and pair of feet clipped from another card. The Christmas pie in his lap is from still another card.
In making pictures of this kind, figures that were originally standing may be forced to sit; babies may be placed in arms which, on the cards they were stolen from, held only cakes of soap, perhaps, or boxes of blacking; heads may be ruthlessly torn from bodies to which they belong, and as ruthlessly clapped upon strange shoulders; and you will be surprised to see what amusing, and often excellent, illustrations present themselves as the result of a little ingenuity in clipping and pasting.
Another kind, which we shall call the
Unlike any other, where the picture once pasted in must remain ever the same, the transformation scrap-book alters one picture many times. To work these transformations, a blank book is the first article required; one eight inches long by six and a half or seven wide is a good size.[67]
Cut the pages of this book across, one-third the way down. Fig. 123 shows how this should be done. The three-cornered piece cut out near the binding allows the pages to be turned without catching or tearing. Leave the first page uncut; also the one in the middle of the book.
Cut from picture-cards, or old toy-books which have colored illustrations, the odd and funny figures of men and women, boys and girls, selecting those which will give variety of costumes and attitudes.
Paste the figure of a woman or a girl on the first page, placing it so that when the lower part of the next page is turned the upper edge of it will come across the neck of the figure where it is joined on to the shoulders.
Cut the heads from the rest of the pictured women, turn the lower part of the next page and, choosing a body as different as possible from the one just used, paste it upon the lower part of the second page, directly under the head belonging to the first body. Upon the upper part of the second page paste any one of the other heads, being careful to place it so that it will fit the body. Continue in this way, pasting the heads upon the upper, and the bodies on the lower, part of the page, until the space allowed for the women is filled up; then, commencing at the page left in the middle of the book, paste upon it the figure of a man, and continue in the same manner as with the women, until the spaces are all used and the book is complete.
[68]The combinations formed in this way are very funny.[69] Old heads with young bodies; young heads with old bodies; then one head with a great variety of bodies, and so on.
The first picture may represent a man, tall, thin, dressed in a rowing costume, as shown in the illustration. Turn the lower part of the next page, and no longer is he thin and tall, but short and stout, the position of this body giving the expression of amazement, even to the face. The next page turned shows him to be neither tall nor short, thick nor thin, but a soldier, well-proportioned, who is looking over his shoulder in the most natural manner possible (Fig. 124).
The figures in Fig. 124 were cut from advertising cards, and the head belongs to none of the bodies.
A curious fact in arranging the pictures in this way is that the heads all look as though they might really belong to any of the various bodies given them.
Instead of having but one figure on a page, groups may be formed of both men and women, and in the different arrangement of the figures they can be made very ludicrous indeed.
Mix one-half cup of flour with enough cold water to make a very thin batter, which must be smooth and free from lumps; put the batter on top of the stove—not next to the fire—in a tin saucepan, and stir continually until it boils; then remove from the stove, add three drops of oil of cloves, and pour the paste into a cup or tumbler. This will keep for a long time and will not become sour.
Just a glance at a pile of ordinary every-day kindling wood could hardly suggest to one the possibilities existing in the crude material for building all sorts of interesting and realistic things for the little folks, but experiment and you will find that Klondike log-houses, rail-fences and lumber camps, bridges, and substantial little rafts which will float on water in laundry or bath tub, pond or stream, can be easily and readily built from the little sticks we use to start our fires.
Let us build
Select two sticks of kindling wood as near of a size as you can find, and lay them side by side, a short distance apart; then connect the two by placing sticks across the ends, log-cabin fashion. These four sticks form the square foundation of one bridge pier.
Continue building by crossing the second layer of sticks with a third layer, the third layer with a fourth layer, and so on until the pier is built up sufficiently high, six or more layers, according to the thickness of the sticks. As you build be sure that the two sticks forming each layer lie absolutely steady and are of about the same thickness, that those built on top of them may not slant, but lie level and steady.
All sticks should be of the same length, but the layers may vary in thickness; one layer of sticks might be thin and the[71] next thick; it matters not, provided that the two forming the same layer are nearly of a size.
When the first pier is finished, build a second one like it a short distance from the first one, and lay a strip of stiff pasteboard, cut from an old box, across from pier to pier; then lay a second strip of pasteboard from one pier to the ground, a third strip from the remaining pier to the ground on the opposite side (Fig. 125). If you wish, the two end strips can be longer than those shown in the photograph, and slant from the piers down to the ground on a level with the water. The banks in the photograph are built up with boxes and covered with green cloth.
For each of the two archways, take two thin sticks of wood and stand them at the top outward edge of the pier, with ends braced together at the top, and spread out at the bottom, as in the photograph.
Use either natural or tissue-paper trees stuck into empty spools for foliage, or little toy trees, if you happen to have them among the children's store toys.[72]
Though the bridge is not intended to be over real water, you might try the experiment and strengthen the hollow piers by filling them with stones, when building the bridge out-of-doors.
Fig. 126 shows two little
Place one end of a second stick up against one tie, allowing one string to come over and the other string under the second stick (Fig. 128). Cross the two lengths of the string over the second stick, bringing the lower string up and the upper string down (Fig. 129); then lay another stick up against[73] the crossed strings, carrying the strings in turn over this stick (Fig. 130). Again, bring the lower string up and the upper string down, before placing another stick. Continue crossing the string and adding kindling wood until the raft is of the desired length. Tie the ends of the string securely on the last stick, and weave the opposite loose ends of the sticks together in the same way, tying the string firmly together on the last stick. Clip off the ends of the string and the raft will then be ready for the water, and will carry either passengers or freight.
Put up log-houses for the toy people to live in. Select two different lengths of kindling wood for
Place two long sticks of kindling wood a short distance apart and running parallel; across these sticks lay two shorter ones, bridging the space at each end between the long sticks, then place two long sticks over the ends of the two short ones; keep building in this way until the little house is seven or eight layers high.
Cut a piece of white cardboard or light-weight pasteboard the length of the house, and wider than the width of the house, to allow for the slant of the roof. Bend the roof lengthwise through the centre and lay it on top of the house (Fig. 131). Make a door of stiff pasteboard painted or covered with a layer of brown tissue-paper pasted on the outside. Cut the door a suitable size and stand it up in front of the house.
If you want
Original home-made toy men, dogs, and sled may be used[75] to complete the scene, or they can be cut from newspapers or old magazines. Stiffen by pasting them on cardboard; then cut out the men, dogs, and sled more carefully in detail. Bend one leg forward and one backward to make the men stand alone, and bend two legs outward and two inward to enable the dogs to stand. Paste narrow strips of paper on the dogs for harness.
Make another kindling-wood scene like Fig. 132.
Lay down one piece of kindling wood, and over one end place the end of another stick, forming a rude letter V (Fig. 133). Across the end of the second stick which rests on the ground, place the end of a third stick (Fig. 134). Keep on building the first layer of the fence in this way until it stretches as far as you wish; then go back to the starting point and begin building the second layer of sticks, by placing a stick over the first stick, resting one end on the far end of the first stick, the other end on the top of the end of the second stick; lay another stick across over the second stick, another over the third, and so on until the second layer is finished. Build other layers in like manner, and make the fence high or low, as desired. Pile up kindling wood into a wood-pile with small pieces scattered on the ground, and if there is a toy horse you can make him haul more wood (Fig. 132).
These kindling-wood toys will give a realistic idea of log-houses, rail-fences, log rafts, and primitive bridges, and while building them the children might be told stories of the way early settlers lived and made their homes, or the children may "make up" stories about the different scenes.
Substantial little hammocks which will hold good-sized dolls, and even a real pussy with no danger of the material breaking, can be made of ordinary kindling wood or strips of pasteboard (Fig. 135). Both styles of hammocks are woven in the same manner. The weaving is like that used for the[77] raft and is of the simplest, most primitive kind, merely crossing of the two ends of each side string between each piece of wood (or pasteboard) slat, with loops of string left at each end of the hammock for hanging it up. When fashioned of kindling wood, like that in the photograph, have the sticks slender and all of the same length. When made of pasteboard, cut seven-inch-wide strips from a heavy pasteboard box and cut the strips crosswise into one-half-inch slats. Have ready two long strings measuring about two and a half yards each. Double each string and tie a knot in the closed end, fifteen inches from the extreme folded end, then place your work on the top of the table, or some other flat surface where you can keep the slats flat and even. Begin to weave by laying a slat between the loose ends of each string.
Push the slat up tight against the knots and cross the strings on the outer edge of the slat. Slide another slat between the two ends of each side string, shoving it close up against the crossed strings at the outer edge of the first slat. Bring one end of each string over and one under the second slat, cross them, and add the third slat. Continue weaving in this way until the hammock is of sufficient length, then tie the strings securely at the outer edge of the last slat.[78]
After you have put in the last board bring the slats up very close together and draw the strings firm and tight. Tie the double lengths of string together at each end of the hammock, making two long loops by which to hang up the hammock.
Have you seen the little people who live up in the trees? Little twig people who dance and swing and bob about, who nod and bow and flutter hither and yon; some astride funny twig horses, others dangling head down, many waiting to run a race when a stiff breeze comes along, and all as merry as merry can be, tossing their long, thin arms and legs in the air just for the fun of it. Perhaps some of these queer folk are outside your window now, and it may be near enough to the ground for even the littlest boys and girls to reach if they stand on their toes. Here are several of the twig people who came down and posed for their photographs. We will give each one a name.
Fig. 145 is Miss Daffy-down-dilly, who has just come to town and is feeling very bashful about it.
Fig. 148 is Jack-be-nimble Jack-be-quick, who thinks he can jump over any candlestick, high or low.
Fig. 151 is the Little Crooked Man who ran a crooked mile.
Fig. 152 is Little Miss Muffet, who is so terribly afraid of the spider.
Fig. 153 is Peter White, who follows his nose wherever he goes.
Fig. 154 is Doctor Foster, who went to Gloster in a shower of rain, and he is stepping very high to avoid falling into the puddle we have all heard about.
The little twig people do not look quite as real when separated from the tree as when you see them dancing in the[80] breeze, so it is necessary to help out their appearance with paper heads and hands and feet.
Use care in selecting your twigs, for they are not all alike. Some are quite choice and unique, others more commonplace and less amusing. Suitable ones may be found in plenty.
When a small branch is broken from a tree or bush, you will find that some of the twigs attached look like queer, crooked, little legs, and some, just the right distance above, seem made for arms. Then comes the long neck that is joined, perhaps, to the still larger branch or to the trunk of the tree. Sometimes there are several arms and several[81] legs too many and you must look closely and decide which are the real ones; then cut off the others.
You will know the real
Cut the long neck down in proportion to the rest of the body and trim the arms and legs off to the proper length. Remember that one inch of the neck of the dolls must be inserted in the head and allow for that in cutting the long stem.
Fig. 136 gives a branch as it looks when taken from the tree, and the black bands on the twigs show where they should be trimmed off to bring the little figure into proportions. The parts left white or in outline, below the bands, are to be cut away. There are two legs to this branch and three arms, one of which must be dispensed with. The left arm must remain and it matters but little which of the right arms is selected. In this case the lower one is marked to be cut.
Now comes the making of the
These must all be double, for, to hold them on, the twigs are pasted between the two halves. In some cases, where the neck is quite thick, you will find it best to shave off a little at front and back to flatten it, so that the neck may lie easily between the two parts of the head and not push the face out of shape (Fig. 137). This is seldom necessary, however, unless the doll is unusually large.
Figs. 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, and 143 give the heads of all our little troupe sufficiently large to be copied. Fig. 144 shows the hands and feet.
[82]Use a heavy brown wrapping paper for the heads and draw the faces simply with pen and ink in broad lines, or, if the[83] children want to color them, they can use water-colors or colored pencils. In any case the features should be strongly marked, that the character of the face may not be lost.
You can make the hands of paper like the face, or of dark brown paper (not tissue), to match the dark brown arms. White hands will give the effect of white gloves. Make the[84] feet brown or black, or use bright colored paper to represent colored shoes.
These are the proportions. Of course, for a smaller doll they should be smaller.
Fold a piece of wrapping paper, making it double, and on the paper draw Daffy's head, copying the one in Fig. 138, or making an original head if you prefer. The back hair may be drawn in or painted if the children insist upon having an all-around doll. If the neck is thick shave it off as in Fig. 137. Draw two hands on double pieces of paper and two feet on double pieces of paper, and cut them out. Daffy's hands are the color of her face, and her shoes are black.
Now cover the inside of the back of the head with paste, lay the neck on the head and cover that too with paste (Fig. 137). Then fit the front of the head to the back and press it down until the two halves, with the twig between, are pasted firmly together. In the same way paste on the hands and feet. Make Daffy's dress of yellow tissue-paper, the color[85] of a daffodil. Cut a circle for the skirt with a small hole in the centre and slit it down the back;' then draw it through your hands to shape it and make it hang nicely.
Cut out a little waist with pointed sleeves, like Fig. 146, and a pointed collar, like Fig. 147. Make the waist double with the fold at the top, cut a hole for the neck, and slit down the back. Use green tissue-paper for the collar.
Put the waist on the doll, gather it at the belt line, front and back, and paste. Paste it also at the neck and along the under edge of the sleeves. Paste the skirt to the waist at the belt, bring the edges of the slit together at the back, lap them, and paste. Wrap a strip of the yellow paper around the waist for a belt, then put the collar around the neck, and fasten with a touch of paste.
You will find the Crooked Man's head in Fig. 141. His hands are cut from brown paper, like C (Fig. 144), and his feet, which are also brown, are like E (Fig. 144).
You can make Miss Muffet's dress any color you like, the brighter and gayer the better. Cut the skirt and waist as[88] you did for Daffy-down-dilly, but do not point the sleeves. Make an apron of two squares of white tissue-paper—a large and a small one. Use the large square for the skirt of the apron and the small square for the bib. Gather the top edge of the large square and the bottom edge of the small square, and paste to the dress at the belt line; then make a white belt and tie in a bow at the back.
For the hat, cut a circle of tissue-paper the color of the dress, put a little paste in the centre, and pinch it down on the top loop of Miss Muffet's hair, tipping it a little to one side. This will give a crown. Turn up the brim at the back and lift it in front to stand out straight. Fringe a small piece of black paper for a feather and paste it to the crown of the hat.
Peter White's head is given in Fig. 142. His brown hands are cut like H (Fig. 144), and his black shoes like I (Fig. 144).
This doll is the only one whose head is in profile, but it shows that when the shape of the twig suggests it, a profile is very effective; and it is usually the easiest for children to draw.
From old visiting cards you can build all the different houses and furniture seen in the accompanying illustrations.
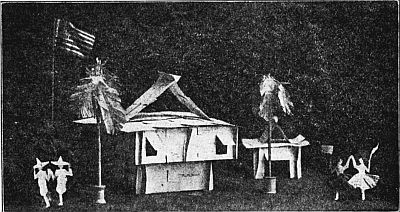 Fig. 156—The little tropical house in Uncle Sam's newly acquired possessions. Made of old visiting cards.
Fig. 156—The little tropical house in Uncle Sam's newly acquired possessions. Made of old visiting cards.
For the little
Place two of the cards together and cut two slashes, one on each side of the centre, through one end of the double layer (Fig. 157). Slide the two cut ends together, allowing the[91] centre divisions, A (Fig. 157), to lie, one over and one under the two cards. This will bring under the side divisions B and B (Fig. 157), on the card whose centre division A comes on top, while the divisions B and B of the other card will come over on the outside (Fig. 158). Fasten all of the remaining cards together in pairs in the same manner; then cut a long slit near the outer edge of each of the four pairs of cards, C and C (Fig. 159). Slide the walls together at right angles, and form a square by means of the long slits. Do this by holding the open end of one long slit in one wall under, and at right angles to the open end of one long slit in another wall, and then fitting the two walls into each other so that they will stand firm and form one corner of the lower story of the house (Fig. 160).
Strengthen the house with an extra inside wall. Cut long slits in each end of the extra wall, then a long slit near the centre of each side wall in which to fit the extra wall.[92]
Make the ceiling of the lower story of two more pairs of cards fastened together like Fig. 158, and on the ends of each pair of cards cut similar divisions, only have them quite short (Fig. 161). Bend down all of the end divisions and fit the strips over across the top of the first story from front to back, bringing the two corner divisions, D and D (Fig. 161), on the outside of the wall, while you slide the centre part, E, on the inside (Fig. 162). Dotted lines indicate the division E on the inside.
The second story must be built entire before it can be fastened on top of the first story.
Make each of the four walls of the second story three cards long. Cut divisions on both ends of the middle card to fit in the end cards (Fig. 163).
When cutting divisions, always fit together the two cards that are to be joined, and cut through the double layer, which will insure having the divisions alike.
When the four walls are ready to be put together, cut a window in the two end cards of the wall which you intend for the front (Fig. 164). Only the lower edge and sides of the window may be cut; the upper edge is merely bent and throws the solid window shutter, formed of the piece cut, outward, as shown in the photograph.
Slide the four walls together and add a fifth wall, to run through the centre from side to side, for strength. Use the long slit method for joining the centre wall to the side walls.
When built, turn the second story upside down and fit a strip of three cards, bridge-like, over the centre from front to back, and fasten it to the bottom of the walls as you attached the ceiling of the first story; then fit on another strip in like[93] manner over the centre from side to side, and fasten it to the bottom of the side walls. The two strips will cross each other at their centres, one lying at right angles over the other.
Carefully lift the second story and adjust it squarely and evenly on top of the first story, as in the photograph (Fig. 156).
Make the projecting roof of the second story of four strips of four cards each. Run the strips from side to side of the house and lap them a trifle, one over the other. The roof is merely laid on and is supported by the walls.
The peak is made of two strips of two cards each, and slid into a base of one strip of three cards by means of long slits. At the apex the cards are also fastened together with long slits.
The little summer-house in Fig. 156 has each of the four sides made of one card. The cards are fastened together[94] by means of long slits. A doorway opening is cut in the front wall, much in the same manner as the windows are cut in the large house, only in this case the incision is made directly on the lower edge of the card, and, when finished, the lower half[95] of the door is cut off. The door is bent outward and forms a little canopy for the open doorway, as in the photograph.
Make the roof of two strips of cards of two cards each by merely laying the strips across the top opening of the house.
Fasten the ends of the two cards together with long slits to form the apex of the peak, and bend the bottom ends of the cards out flat, so the peak will stand steady on the roof.
If the children would like to keep the buildings intact to play with at any future time, as they build up the structures let them add a little glue or strong paste here and there to hold the various parts firmly together. The toys will then last a long time and stand considerable wear.
Tissue-paper trees in spools furnish the foliage in the photograph, while a miniature flag, with its pole supported in an empty spool, shows the nation to which the country belongs.
Cut little paper people from cardboard and place them on the grounds.
A fine setting for the scene can be made by tacking a piece of green canton flannel, fleecy side uppermost, taut over a pastry board, or pinning it on a piece of the light-weight patent straw pasteboard.
The fleecy green gives the appearance of grass, and when the glistening white buildings are set down on the grass among the trees with Old Glory floating overhead, and gaily dressed dolls in the foreground, the children will be delighted with the scene; nor will the appreciation be confined to the children, for older people will also enjoy it.
The best framework for a newspaper wigwam can be made of long-handled feather dusters, but long-handled brushes, or poles of any kind you may happen to have, will answer the purpose; all that is necessary is something you can make into a framework similar to Fig. 168. Tie your poles together at the top and spread them out at the base, tent-fashion.
Make the
Only three poles will be needed when the covering is of newspaper, but if you do not happen to have enough newspapers on hand for the entire outfit of tepees and costumes, you can use a white muslin sheet for the wigwam, in which case four poles will be needed (Fig. 169). The sheet, not being stiff like the paper, requires more supports to make it stand out sufficiently. Should it be inclined to fall in between[99] the poles, pull it out a little and lay a book over the edge which lies on the floor, as a weight, to keep the sheet in place.
If you would like the wigwam decorated in real Indian fashion, cut out large colored paper pictures and paste them around the lower part of the wigwam, forming a band of pictures. Be the covering either cloth or paper, it will look well decorated, but the covering must be taken off and the pictures pasted on. The covering should then be adjusted over the poles. One great beauty and attraction of this[100] newspaper Indian material is that effective results can be produced quickly and with little work.
Make
Fringe the central portion of the longest edge according to the fringe lines on Fig. 170. Cut the two boundary lines of fringe, A and A, up to the dotted line; then bend down all dotted lines. Bring the two ends together, allowing the fringe to come on the outside, and fit the point B over the other point B. This finishes the newspaper moccasin (Fig. 171).
Make
Use one sheet of paper for the little fringed sacque. Allow the paper to remain folded along the white central band, and fold the double layers crosswise through the centre, making four thicknesses. Cut an opening for the head according to dotted line C (Fig. 172). Fringe the sides along dotted line D, as shown in diagram (Fig. 172).[101]
Unfold carefully, that the paper may not tear, and after cutting a slit from the neck partially down the centre of the front, you will have Fig. 173. If you wish to make the garment less liable to tear, paste narrow strips of muslin on the under side of the sacque, around the neck, down each side of the slit, and at the head of the fringe.
From a folded piece of newspaper cut the little squaw a head-dress (Fig. 174). Let the top of the feather come on the fold of the paper. Turn over and crease down the straight edge of the band at the dotted line (Fig. 174), making four layers.
Crown the little girl with the head-dress, pinning the ends together at the back with a safety-pin. Slip the moccasins on her feet, fastening them to the toe of the shoe with a little stiff paste, and your[102] charming little squaw will be ready to play in the wigwam (Fig. 175).
Older girls can make the Indian costume from the same patterns by cutting them larger.
The Indian boy needs a lot of fringed newspaper for his costume. Cut folded strips to make the fringe thick and in two layers. Fold down the solid edge of one strip and with safety-pins fasten the fold along the outside line of the boy's trousers and stockings, as in the photograph (Fig. 176). Trim the other trouser leg and stocking in the same manner.
Cut a generous strip of double-layer fringe to fasten entirely around the boy's shoulders, extending across both back and chest. Reinforce the top edge of the band of fringe, and along the line where the solid paper meets the fringe, with strips of muslin, pasted on, to prevent tearing.[103]
For the chief's
The open base of the band lying against the boy's back causes the feathers to stand out and not fall flat and spoil the[104] effect, as they otherwise might do. The photograph of the boy chieftain standing was taken expressly that you might see exactly how the newspaper costume of the Indian brave should look.
Make the
When the corner roll is the right size, continue to roll the paper until a long round stick is formed (Fig. 181). Paste the loose end of the stick on the roll and cut both ends off even, as indicated by the dotted lines in Fig. 181.[105]
Bend the paper roll about six and a half inches from one end, and bring the bent portion over against and on top of the roll. Pin the fold down on the roll three inches from the bend; then turn up the open end to form the bowl of the pipe, which you must make stand erect should it seem inclined to lean (Fig. 182).
Fig. 183 is the photograph of a Christmas tree whose trimming is entirely home-made. The brilliant colors and shining gilt of the papers used, give a sparkle and life that are most captivating, and the ornaments are so easily made that the children themselves can do much toward decorating a tree in this manner.[107]
At the top of the tree, shining above all other ornaments, is
From a piece of cardboard cut an oblong with the top and bottom edges five and a quarter inches long and the side edges just five inches long (Fig. 185). Now, exactly in the middle at the top edge, make a dot, A (Fig. 185); then on each side edge make a dot, BB (Fig. 185). On the bottom edge, one inch from each bottom corner, make the dots CC. With the aid of a ruler draw the lines connecting these points, as shown in Fig. 185. This gives a perfect five-pointed star, five inches high. Cut the star out, cover its entire surface with a coat of paste, and lay over it a smooth piece of gilt paper, pressing out the fulness and creases. When the paste is dry, cut away the paper from the edges, and there will remain a gilt star, firm and stiff enough to stand up bravely.
But this is not all. There are to be a number of gold-tipped rays flaming out from the star to represent its spreading light. For these rays select ten broom straws with two prongs. Trim the prongs evenly, shorten the stems at the bottom, and spread the prongs apart (Fig. 186). Now, cut twenty strips of gold paper half an inch wide and a little over four inches long. Lay one strip down, cover the wrong side with paste, place three broom straws with their prongs resting on the paste side of the paper, and press another[108] strip of gold paper over the first, inclosing the tips of the straws. This will give a gold paper on both sides of the straws. Then, when the paste is dry, cut away the paper, leaving a gold triangle on the tip of each prong of each broom straw. Fig. 187 shows one triangle cut out. Treat all of your broom-straw rays in this way, then cover with paste the centre of the wrong side of the star up to the points, lay two straws in place, the stems crossing, as in Fig. 188, and over the stems press a short strip of white paper, like D (Fig. 188), pasting it down securely. Adjust the other rays between the points of the star, and fasten in place in the same manner.
To hold the star upright, make a lighter from a strip of white writing-paper for a stem. Flatten the top of the lighter, cut it off evenly, and paste it on the back of the star between the two lower points, as in Fig. 188. Over the stems of the broom straws and the end of the lighter paste a white paper lining that will reach part way up each point of the star. This lining should be made[109] before the rays are pasted to the star, by laying the star on white paper, tracing around its edges with a pencil, cutting out the white paper star, and then clipping off about one inch of the points. The gold star will look like Fig. 184.
Not the least effective trimmings on the tree are the little
For a bell three and a half inches high (a very good size), cut a strip of paper three and a half inches wide and seven inches long, curve it into the cone shape shown in Fig. 190, and pin together. Cut off the point that laps over, according to the dotted line, also the point that laps under, leaving a little over half an inch for the final lap. Trim off the bottom points even with the shortest part of the bottom edge, as shown by the curved, dotted line, and you will have Fig. 191. Fig. 191 opened out will give you Fig. 192, which will be the pattern for other bells.
As Fig. 192 lies flat on the table, run the paste brush along one side edge, making the coat of paste as wide as the lap is to be, then curve the bell into shape. Make the bottom edges meet evenly and press the paste-covered edge over the other side edge. Hold the finger inside the bell while you do this, to keep it from flattening.
The clapper is made of two round disks of gold paper with the string pasted between them. For the bell we are now making, the clapper should be almost one inch in diameter. Fold a piece of gilt paper and cut out the two disks at one time (Fig. 193). Cover the wrong side of one disk with paste, lay the end of a string across the middle (Fig. 194), and press the other disk on top. Both sides of the clapper will then be gilt. Hold the clapper up to the bell by the[111] string, so that half of the clapper is below the bottom edge of the bell; then, bringing the string close to the point at the top of the bell, run a pin through the string to mark the distance. Where the pin is, tie a knot, F (Fig. 194); this is to hold the clapper in its proper position. Thread the end of the string through the eye of a darning-needle and push the needle up through the point of the bell—the knot will keep the string from running up too far (Fig. 195). Allow eight or ten inches of string above the bell, so that it may be hung high or low, as[112] desired. A bell should never be tied close to a branch, but should hang down far enough to sway with every passing current of air. The long string also adds to the decorative effect.
Cut a strip of white tissue-paper five and a half inches wide and twenty-two inches long. Fold the paper crosswise through the middle; then fold it again and again until your folded piece is one inch wide. The folds must always be across the paper from start to finish (Fig. 197). Now, cut slits in the folded paper, first a slit on one side, and then a slit on the other, as in Fig. 198. Let the spaces between the slits be one-eighth of an inch wide, and cut each slit to within one-eighth of an inch of the edge. When this is done, carefully unfold the paper and spread it out flat, then lift the top edge with one hand, the bottom edge with the other, and gently pull the meshes apart. Gather the top edge into little plaits, and twist them together in a point; gather the bottom edge in the same way and twist that; then carefully pull the snow pocket out, and you will have a long, narrow bag of soft, white meshes. If it flares out too much, crush it together softly with your hand. Make a small gilt paper star and fasten a narrow strip of white tissue-paper to its top point. Open the bag, slip the star inside, and suspend it half-way from the top by pasting the end of the paper strip to the top of the bag. Make a loop of tissue-paper, fasten it to the top point of the bag, and then hang the snow pocket on the tree. The gold star gleaming through the frosty meshes is very pretty, but if you have several snow pockets, there need not be stars in all.
Thread a clean, cotton string in a large darning-needle, then select three of your largest raisins for the body and a suitably shaped one for the head. There must be three raisins for each leg, one for each foot, and three for each arm. Tie a knot in the end of your string and, beginning with one foot, string on three raisins for one leg, then the three for the body, and, lastly, the one for the head. Tie a knot close to the top at the head and leave a long end to the string. Thread your needle again and string on the raisins for the other foot and leg, then run the needle up through the lower[115] raisin of the body, and fasten the second string to the first between the two body raisins.
String three raisins for one arm, run the needle through the middle of the top body raisin, where the shoulders should be, then string on the three raisins for the other arm and tie a knot at the end. Jocko is all right now, except that he is very limp. Put stiffening into his joints by running broom straws through his legs, body, and arms. Use a raisin stem for the tail, and fasten it on by pushing the largest end into the lowest body raisin. Make the eyes by running a short piece of broom straw through the head, allowing the ends to stand out a short distance in the place for the eyes. Remember a monkey's eyes are always close together, and they must be made so in order to look natural.
At this stage Jocko will resemble Fig. 200; but he must have clothes and a hat to give the finishing touches and make him look like the monkeys the children are familiar with. Fig. 201 is Jocko's hat, Fig. 202 his coat, and Fig. 203 his little skirt.[116]
Cut all of these from bright-colored cambric of a size to fit the monkey. Fold a piece of cambric for the coat, and cut it out as you would for a paper doll, with the fold at the top. The skirt and hat are circular. Cut a round hole in the middle of the skirt for the waist, and slit it down the back. This furnishes the costume.
Now, thread the end of the string from the top of Jocko's head into the darning-needle and run the needle through the middle of the hat (Fig. 200); then push the hat down on his head. Fit the skirt around Jocko's waist, and fasten it at the back with needle and thread; then put on his jacket and fasten that in front. It is unnecessary to say that Jocko is good to eat.
Strings of
Fig. 209 shows how these strings are made. Red, gold, yellow, orange, green, blue, and white make pretty disks, and show off well on the tree.
Cut your disks perfectly round, and in pairs; for they must be the same on both sides, G, H (Fig. 209). You can make the disks on some strings all of one size; on others they may graduate down to quite small ones at the ends. When the disks are cut out, lay one down, bottom side up, H (Fig. 209). Cover this with paste, then lay a white cotton string across the disk, directly through the middle. Allow about six inches of the string to extend beyond the disk, and let each string be one yard long. Before the paste has time to dry, press the mate of the disk, G (Fig. 209), on top of H, over the string, taking care to have the edges even. Go through this process with each disk. Paste them on the string one inch apart, and leave six inches of string at the last end.[119]
Fig. 210 is a dainty
The crowning glory of every Christmas tree is its
Fig. 213 shows some paper candles on an evergreen branch, standing upright and burning briskly. The candles may be made of white as well as colored paper. Make an oblong, K (Fig. 214), four inches long and two and a half inches wide, the wick one-quarter of an inch high, and the back of the flame, L, three-quarters of an inch long. From orange-colored tissue-paper cut the flame (Fig. 215). This should be a little over a half an inch wide at the base and two inches long. Lay an oblong on the table in front of you; take a[122] large-sized pencil; place it on the long edge farthest away from the flame, and roll it on the pencil (Fig. 216) until the opposite edge overlaps the roll. Then run the paste brush along the edge and paste it down. Your candle is now a hollow roll. Slip the roll off the pencil and cut two slim notches opposite to each other, in the bottom edge (Fig. 217). Make the notches on some of the candles at the front and back, on others at each side. This is so that the flames may always face outward, though the branches that hold the candles may turn in various directions. Lastly, paste the[123] flame on the back of the flame, allowing the tip to flare out at one side as though stirred by a current of air (Fig. 217).
In placing the candles, stand them up astride the branches by means of the notches at the bottom, turning the right side of the flame always toward the room. The tiniest twigs will hold these paper candles easily, and when the needles of the fir interfere with their adjustment, pull off some of the needles and set the candles astride the bare places on the branches.
Finish the tree by throwing over it a web of long, very narrow strips of white and orange-colored tissue-paper.
The narrower the strips the better they will look.
It hardly seems necessary to offer a word of caution, but it will do no harm to say that the flame of gas, candle, or fire, should not come near this paper-decked tree, though it is scarcely more inflammable than a tree trimmed with tinsel.
"Merry Christmas! Merry Christmas!" calls out Santa Claus cheerily as the guests come trooping into the room.
Laughing and joking, his eyes twinkling with fun, Santa Claus names each person as he hands out the gifts from his fat Christmas bag and from the generous pile at his feet. All this merriment happens at Christmastide when you play the part of good "Kris Kringle" in your own home, in the schoolroom, the Sunday-school, or in any place where Christmas is celebrated and where children are gathered to enjoy the festivities.
Take a good long look at Santa Claus, as shown in the picture (Fig. 218); then turn your eyes to the illustration (Fig. 219). Can you believe it possible that the two photographs are of the same person in identically the same pose? Such is truly the case. The second gives the woman's back, while the first shows her face, arms, and hands transformed into those of the jolly saint.
You can see at a glance how very easy it will be for you to have a real, live, little Santa Claus for your Christmas.
Any one—grandfather, grandmother, father, mother, big sister or brother, or you yourself—can assume the character of this live little saint, can grow suddenly short of stature, jolly and fat, be arrayed in scarlet, ermine-trimmed, and crowned with a red-peaked hat, all in less time than it takes to tell it; and, stranger still, the transformation may be accomplished in a very comfortable way, without even the bother of changing the usual attire.[125]
It is essential merely to paste on the face tufts of raw cotton for eyebrows, mustache and goatee, and to slip over each arm an extra sleeve. This accomplished, and the proper position taken behind the curtain, lo, "magic change"! There you are as fine a little Santa Claus as any one would care to see, and your best friend would not recognize you, so complete is the change. Disguise your voice and no one can find you out, not even your nearest relative.
When the gifts have been distributed and you are ready to go out among the excited children or family circle again, step from the curtain, pull off the extra sleeves, remove the cotton from your face, and in a moment's time you will again be your own natural self.
When preparing this entertainment you will find the demand on your purse very slight, the principal outlay being[126] for the curtain. Purchase moss-green lining cambric, at four, five, or six cents a yard, to stretch over the doorway you intend to use. Two yards and a quarter cut in one full breadth and one half breadth, when sewed together into a curtain, will be enough for an ordinary doorway. Doorways vary in size, however, and it is best to take the measurements of yours before buying the material. The space between the folding doors will probably call for five yards of cambric. When the strips of cloth are sewed together, stretch the curtain taut over the opening, tacking it at long intervals on the topmost level of the wood-work over the door and on the extreme edge of the door jamb next to the wall. If fastened in this manner, tacks will not injure the wood-work.
Stand on the floor facing the centre of the curtain and mark the place where your face comes; then where your arms will most easily pass through the curtain. Cut holes in the cloth, one for your face with chin entirely through, and two for your arms (Fig. 220). Cut the holes small; they can be enlarged if necessary.
Make Santa Claus's cap of a piece of scarlet cambric twelve inches wide and seventeen inches long; tie one end[127] with a string into a tassel; then pin the cap on top of the face opening (Fig. 221), and cut the lower edge into a curve to fit the hole as indicated by the dotted lines in Fig. 221. One width of scarlet cambric twenty-six inches long, used just as it comes, will make the jacket.
Draw in one edge of the coat to meet the inner edge of the armhole and pin it there; do the same with the other side, and you will have fulness in front to allow for padding. Bring the sides around the armhole outward again and pin in place; then fold up a wide hem and pin the sides of the jacket to the curtain and fill out the inside of the jacket with half sheets of newspaper lightly crumpled (Fig. 221).
Pin enough paper to the curtain under the coat to give the body of Santa Claus a decidedly rounded appearance; be sure that the padding is securely fastened to the curtain. Then pin the sleeve caps, cut according to Fig. 222, around the outer edge of the armhole. Pin raw white cotton around the face opening to form the hair and long, full beard. Allow the cotton to come well over the edge of the hole, that it may lie naturally on Santa Claus's face.
With ink, mark the fleecy side of the strips of white canton flannel to resemble white ermine. Notice particularly the shape of the black ermine dots and have yours like them. Pin one ermine strip down the front of the red jacket and another across the bottom edge. Make two long, separate scarlet sleeves, unhemmed at top and bottom, and pin a band of ermine around each for a cuff. The only necessary sewing for the entire costume is the seams of the sleeves.
Polish up a pair of ordinary old shoes, stuff them out with newspapers, and use them for Santa Claus's feet. Roll two pieces of cardboard, or pieces of limber pasteboard boxes, into cylinders; ink or blacken them. When dry, cut a curve in one end of each, like Fig. 223, and fit these tops over the stuffed shoes to make them into boots. [128]Set the boots on a bench or a low table, placed across in front of Santa Claus, and adjust[129] them under the coat, so the little fellow will appear to be standing on the bench (Fig. 224). Pin Christmas greens, either natural or of tissue-paper, over the top and down the sides of the curtain, and you will have a unique, very effective, and novel arrangement for Christmas, easy to make, and costing but a trifle. Try it.
A natural flower, some tissue-paper, a pair of scissors, a spool of thread, and nimble fingers are all you need.
There are no patterns, only circles and squares and strips of paper which you gather here, spread out there, wrap and tie somewhere else, and, with deft fingers, model into almost exact reproductions of the natural flower before you.
With its unfamiliar terms to be committed to memory and the many parts of the flower to be distinguished, botany is apt to prove dry and tiresome to the little child, but to study nature by copying the flowers in this marvellously adaptable material is only a beautiful game which every child, and indeed many grown people, will delight in. The form of the flower, its name and color, may, by this means, be indelibly stamped upon the memory, and a good foundation laid for further study.
Ordinary garden flowers and those most easily procured make the best models. The carnation, the morning-glory, and the rarer blossoms of the hibiscus are well adapted to the work, also the daffodil and some of the wonderful orchids.
Even holly, with its sharp-spiked leaves and scarlet berries, and the white-berried, pale green mistletoe may be closely copied. All these and many more are made on the same[131] principle, and in so simple a manner that even quite a little child may succeed in producing very good copies from nature.
Buy a sheet of light pink tissue-paper, another of darker pink, and one of the darkest red you can find; then a sheet of light yellow-green and one of dark green. Have a table "cleared for the action" and place your paper on the right-hand side, adding a pair of scissors and a spool of coarse thread, or, better still, of soft darning cotton.
With all this you are to copy the
Lay your natural flower down on the left-hand side of the table, away from your material, but within quite easy reach, for it must be consulted frequently. Seat yourself comfortably and don't work hurriedly.
The first thing necessary in this system of squares and circles is to know[132]
Cut a square the size you wish to make your circle. That is, if you want a circle with a diameter of four inches, cut a four-inch square (Fig. 226). Fold the square diagonally through the centre according to the dotted line on Fig. 226, and you have a triangle (Fig. 227). Fold this at the dotted line and it will make another triangle (Fig. 228). Again fold through the middle and you have the third triangle (Fig. 229). Fold once more and Fig. 230 is the result. Measure the distance from the edge, B, to the centre, A, in Fig. 230, and mark the same distance on the other side of the triangle shown by the dot, C (Fig. 231). With your scissors cut across from C to B, curving the edge slightly, as shown by the dotted line from C to B (Fig. 231). Fig. 232 is the circle still in its folds. Fig. 233 is the circle opened, the dotted line indicating where it has been folded.[133]
Your eye will soon become sufficiently accurate to enable you to gauge the distance from A to B, and you can then cut from C to B without measuring.
Now hold the pink off at arm's length. The separateness of the petals disappears and you see them only as a mass; the points on the edges are not noticeable except as they give the flower a crimped appearance, and the edge of the calyx looks almost straight. It is this appearance or the impression of the flower that you are to produce rather than its many and little separate parts. So now set to work.
From your light green paper cut a circle measuring three[136] and a quarter inches through its diameter and cut it in two to make the half circle for the calyx (Fig. 238). Remove the thread that holds the flower just below its petals and wrap the calyx closely around the lower part, tying it at the bottom; then cut a narrow strip of dark green paper and wrap it spirally around the stem, beginning at the top (Fig. 239). Let the wrapper extend a little below the lighter and twist the end to hold it in place. Spread the petals of your flower as much like the natural blossom as possible.
For the leaves cut a strip of dark green paper six inches long and three-quarters of an inch wide (Fig. 240). Find the centre by folding the paper end to end and making the crease shown by the dotted line in Fig. 240. Gather it along this line, not with needle and thread—we use no needle in this work—but with your fingers, and pinch it together; then twist each end into a point (Fig. 241). With the sharp end of your scissors punch a hole directly through the centre, E (Fig. 241), and push the point of the stem through the hole, bringing the leaves as far up on the stem as you find them on the natural flower; then wrap and tie them in place.[138]
It is wonderful how very natural these blossoms appear. At a short distance no one would think they are not the real, old and familiar pinks. Only the fragrance is missing, and that may also be supplied and a spicy odor given by inclosing a whole clove in the heart of each flower.[139]
From the pale pink paper you can make a delicately beautiful morning-glory (Fig. 244). Have the natural flower with its stem and leaves to copy from, even if the blossom is not the color you want. As with the pink, it is the general form and appearance we strive for in the morning-glory, not the detail.
Make your pink circles with a diameter of about seven inches. It is always better to have your flowers a trifle larger than the natural ones, rather than smaller.[140]
But one circle is required for each morning-glory. Crimp this in your fingers and draw through your hand as you did the circles for the pinks; then, pinching it together to within one and a half inches of the edge, hold it in your left hand and flatten out the top, as in Fig. 245. See that the fulness is evenly distributed, and pull and straighten out the edges until you are satisfied with its appearance.
A piece of bonnet-wire makes the best stem if you wish to give the true viny effect of the growth. If it is only the blossom you are making, a paper lighter will answer. When you use the wire, bend one end over to form a small loop; this is to keep the stem from slipping through the flower. Pass the straight end of the wire through the centre of the flower and draw it down until the loop is hidden.[141]
Make
Make several buds of the pink paper, following the directions given for the green bud of the pink; then twist each bud at the point and add a calyx.
The wilted flower shown in the illustration is made by taking one of the morning-glories you have just finished and actually wilting it by drawing the flower together and creasing and pressing it to resemble the partially closed and drooping natural blossom.
Only a piece of dark green paper six inches square is required to model two almost perfectly shaped morning-glory leaves.
Fold the square twice diagonally across from corner to corner to find its centre; then begin at one corner and gather along one of the creases until you reach the centre (Fig. 251). Start again at the opposite corner, gather along the crease to the centre, then wrap and tie (Fig. 252). Pinch each leaf from underneath along the crease in the middle, to give the depression at the midrib. Straighten the leaf out a little at its widest part and you will find you have a pair of leaves which are surprisingly natural. Wrap and tie these to the stem and make as many more as you think are needed.
Obvious punctuation errors repaired.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Little Folks' Handy Book, by
Lina Beard and Adelia B. Beard
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK LITTLE FOLKS' HANDY BOOK ***
***** This file should be named 25462-h.htm or 25462-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/2/5/4/6/25462/
Produced by Chris Curnow, Joseph Cooper, Emmy and the
Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.net/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.net),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.net
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.